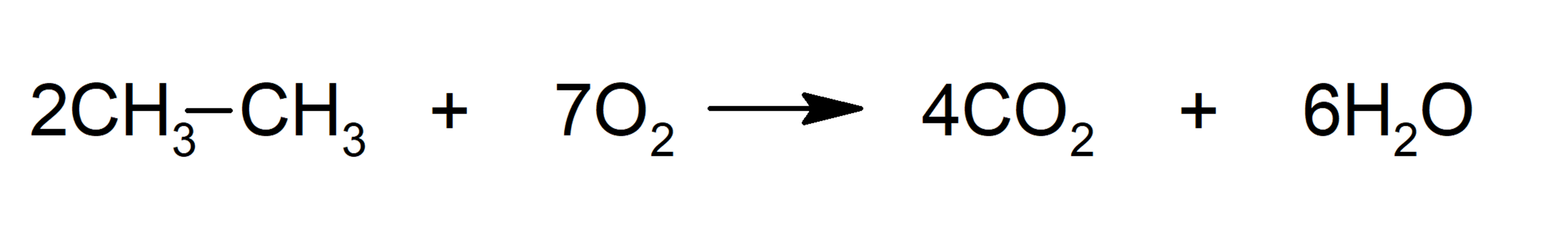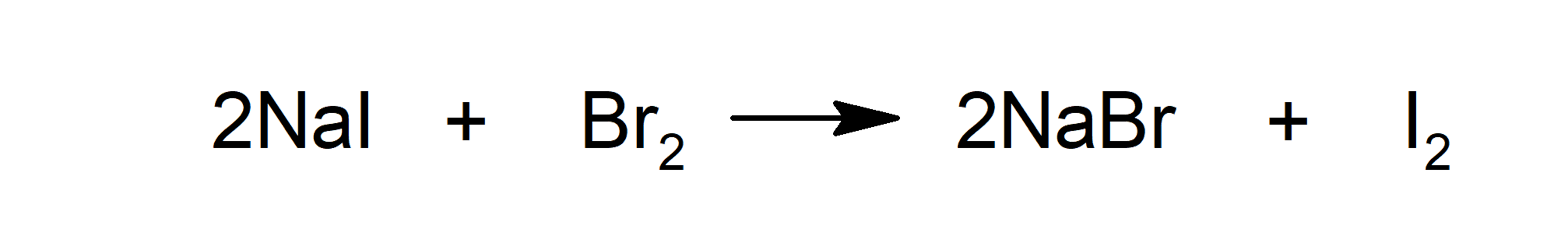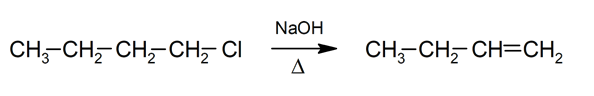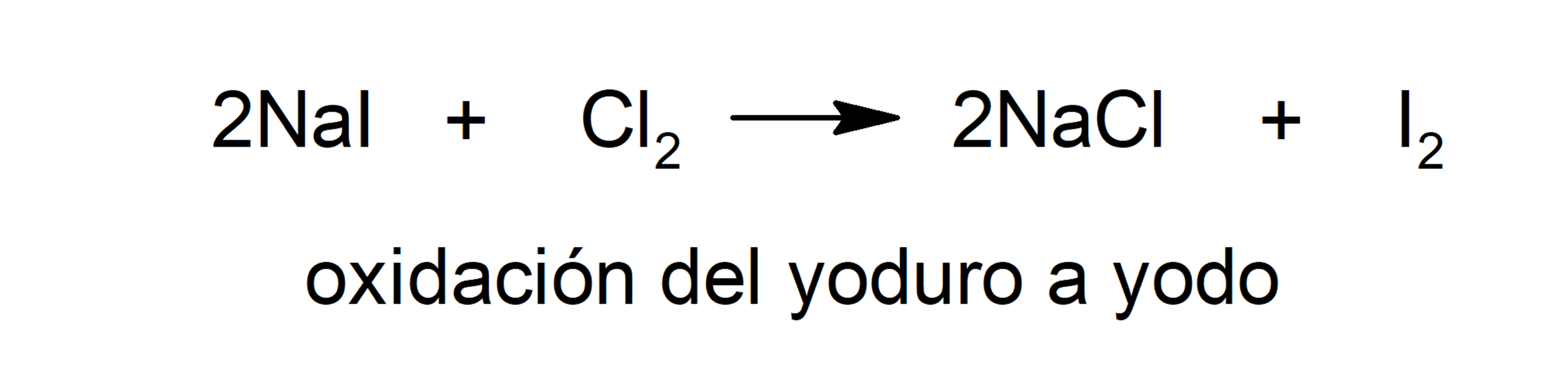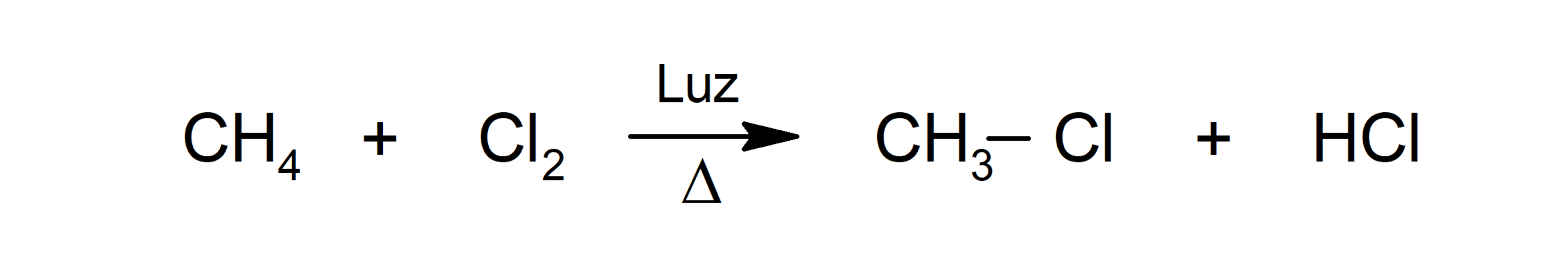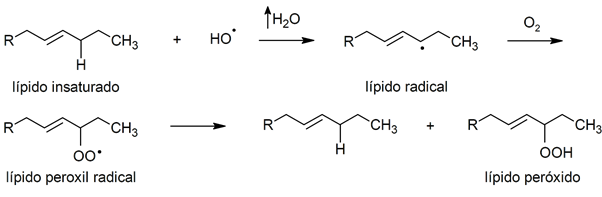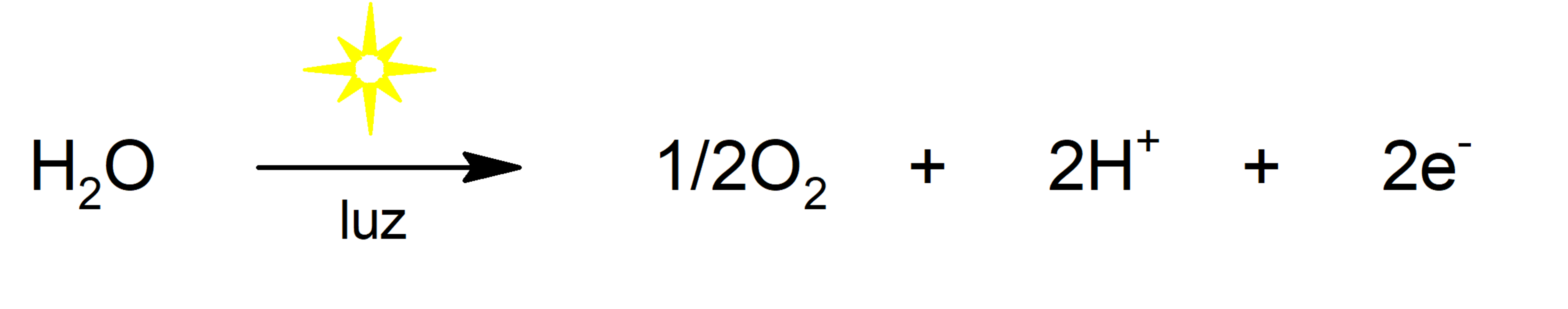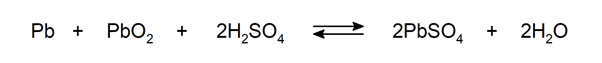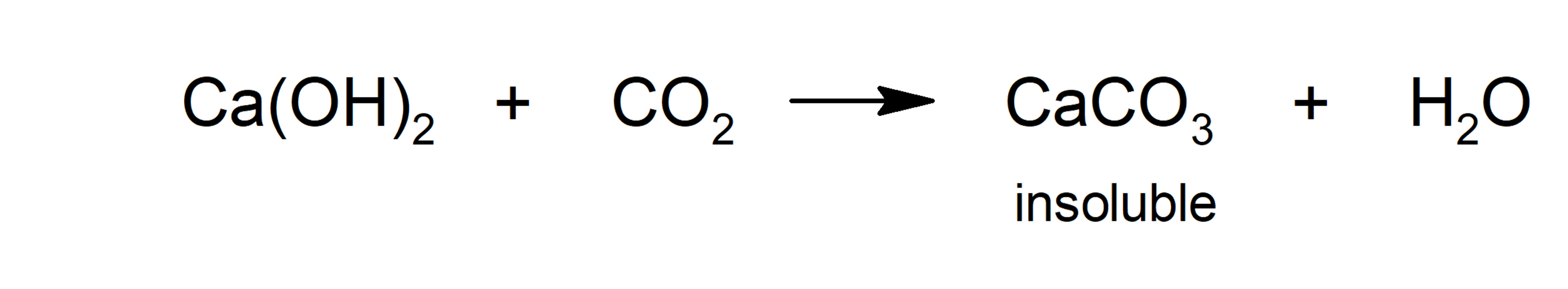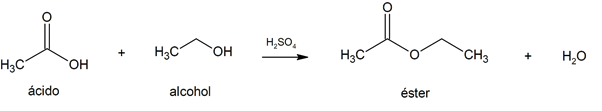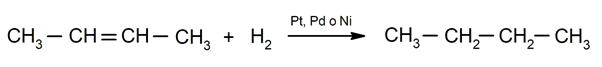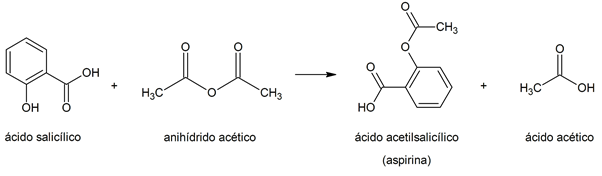It is called chemical reaction the process by which one or more chemical substances (called “reagents”) are transformed and give rise to others (called “products”). Thus, for the reactants to generate the products through a chemical reaction, a reorganization of atoms and molecules must occur in which an exchange of energy occurs. For example: combustion, oxidation, acid-base reactions.
The chemical compounds they have chemical energy in the bonds between the atoms that compose them. Chemical reactions are usually expressed through equations, where the reactants are indicated on the left and the products on the right, linking both parts with an arrow to the right if the reaction is reversible or a back and forth arrow if it is. a reversible reaction.
When the quantities or proportions in which the reactants react and the products are obtained are indicated, we speak of stoichiometric reactions.
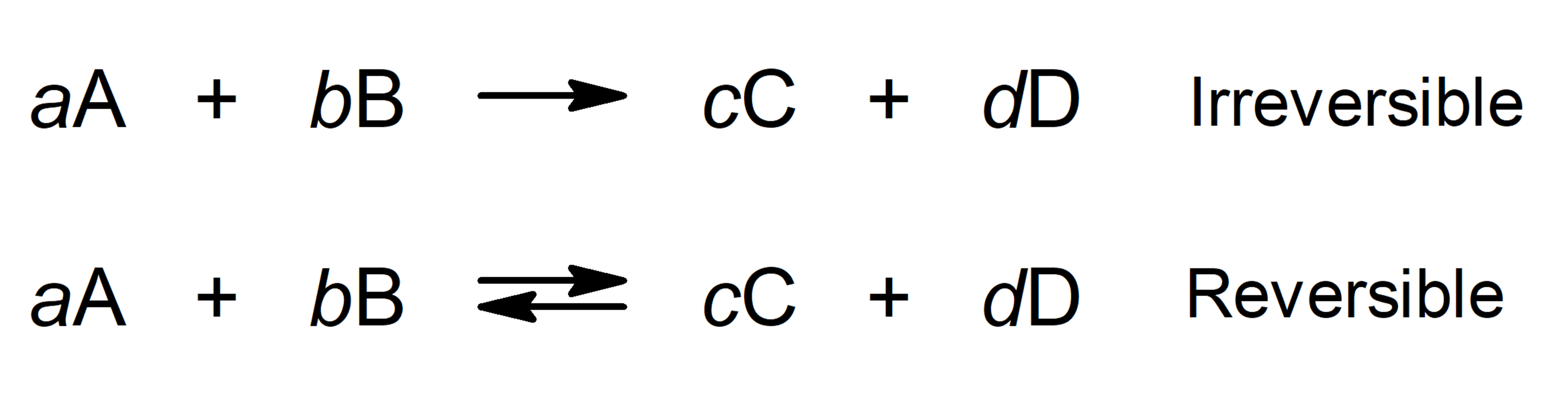
Where:
- A and B are the reactants.
- C and D are the products.
- a, b, c, d are the stoichiometric coefficients (number of molecules or atoms of a certain type that participate in a chemical equation).
chemical reactions can be classified depending on the type of energy they release or absorb. In this sense, they can be exothermic or endothermic (if they release or absorb heat), exoluminous or endoluminous (if they release or absorb light), exoelectric or endoelectric (if they produce or need electricity).
The laws of chemical reactions
Laws are followed in chemical reactions. The most important is the law of conservation of mass or law of lavoisier, formulated by this chemist in 1774, which postulates that in every chemical reaction the mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products.
It was dalton who completed the explanation of this law some years later, indicating that in a chemical reaction the number of atoms does not vary when comparing the reactants with the products, only their organization changes, so that the mass is conserved.
Another important parameter in chemical reactions is their reaction speed since they do not all take the same time to produce. The reaction rate is defined as the amount of product that appears per unit of time or the amount of reactant that disappears per unit of time.
Although each reaction has a different speed, certain factors can make it tend to increase or decrease: the contact surface between the reacting particles and the temperature are some of them.
Catalysts are substances that increase the speed of a reaction, without changing its structure. Some metals often fulfill this role.
examples of chemical reactions
Chemical reactions occur continuously in nature, in the human body, in factories, in effluent treatment plants, etc. Some examples are:
- Combustion

- Substitution

- Addition

- Elimination

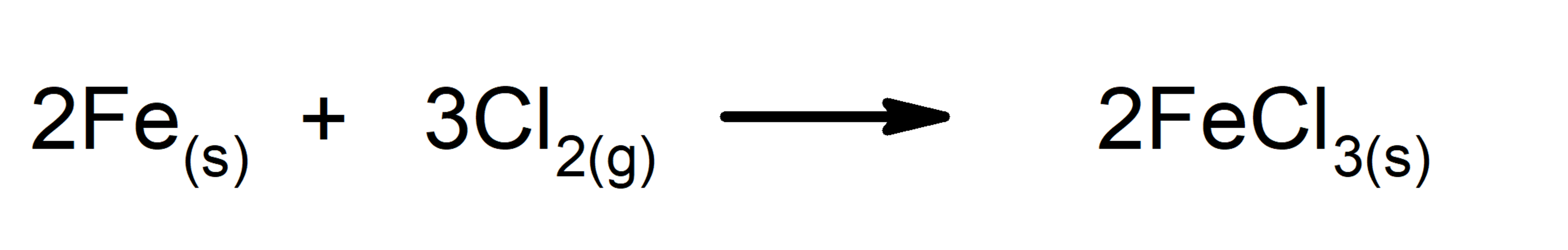
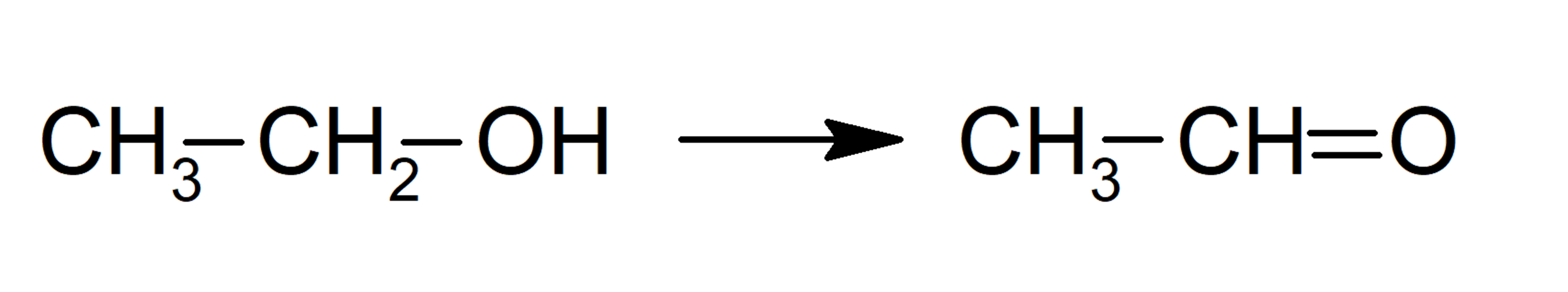
- Oxidation

- Reduction

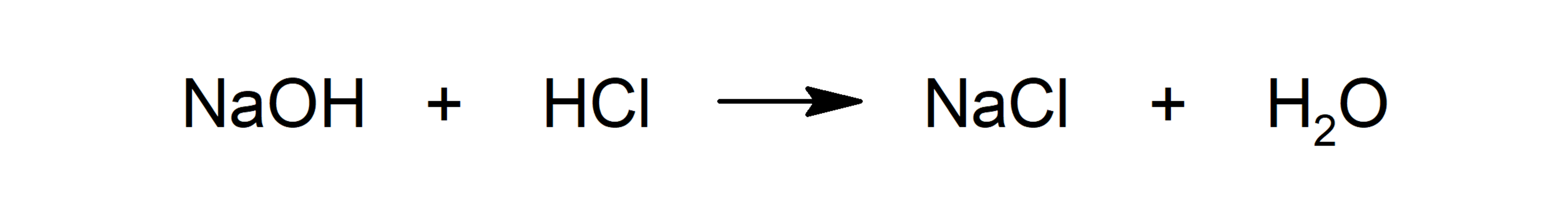
- Acid-base reactions

- oxygenation

- transamination

- Chlorination

- carbonylation

- Nitrosylation. It is a reaction where a nitrosyl group is attached to a protein, after it has been synthesized by the ribosomes.

- peroxidation

- photolysis of water

- Sulfation

- Carbonation

- Ozonation. It is an alternative reaction to chlorination to decontaminate water.
- esterification

- Hydrogenation of alkenes

- Acetylation