The solutions are a type of mixture made up of components that do not chemically react with each other but that can modify their physical properties when they become part of the solution. For example: smoke, amalgam, coffee with milk.

For a mixture to be a solution, it must be homogeneous and uniform. The mixed components cannot be distinguished with the naked eye. In addition, the proportion between the solute (a substance that appears in a smaller amount) and the solvent (a substance that appears in a more significant amount) remains approximately invariable in any volume of solution.
The proportion of the solute in the solution or in the solvent is called “concentration,” and usually, a solution can be prepared using various solute concentrations.
Types of solutions
Solutions can be classified according to their state of aggregation. It is important to mention that solutions can be formed between substances that, before being mixed, are in any of the different states of aggregation of matter: solid, gaseous, or liquid.
Solutions exist in practically all states of aggregation. Generally, the state of aggregation of the solution is determined by the state of aggregation of the solvent.
The types of solutions are:
- Dissolution of gases in gases (soda). For example: the air we breathe.
- Dissolution of solids in gases (soda). For example: dust dissolved in the air.
- Dissolution of liquids in gases (soda). For example: water vapor in the air.
- Dissolution of solids in liquids (liquid). For example: table salt (NaCl) dissolved in water.
- Dissolution of liquids in liquids (liquid). For example: ethanol (CH3CHtwoOH) dissolved in water.
- Dissolution of gases in liquids (liquid). For example: oxygen (Otwo) dissolved in water.
- Dissolution of solids in solids (solid). For example: alloys, such as bronze (alloy of copper and tin).
- Dissolution of gases in solids (solid). For example: hydrogen gas dissolved in palladium.
- Dissolution of liquids in solids (solid). For example: amalgams, which are the dissolution of mercury in other solid metals.
Furthermore, it is usual for the presence of molecules of solute within a solvent to alter the properties of the same solvent. For example, the melting and boiling points of two compounds change when they are mixed, and their densities and colors can also change.
Raoult’s Law
The French scientist Francois Marie Raoult studied the behavior of components in solutions and proposed Raoult’s Law. This law states that the partial vapor pressure of each component in the vapor mixture surrounding an ideal liquid solution equals the partial pressure of each pure component times its mole fraction.
An ideal solution is one in which the chemical species are very similar, so no variation in the energy of the interactions between them is considered. The fundamental equation of Raoult’s Law is:
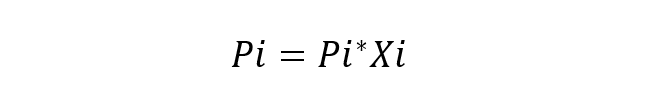
Where:
- Pi is the partial pressure of the component i in the gas mixture surrounding the solution.
- Pi* is the component pressure i.
- Xi is the mole fraction of the component i in dissolution.
Examples of solutions in everyday life
Solutions are mixtures that are present in several areas, both in nature and in the home and in industries. Some of the most common are:
- Air (gas on gas). It is a solution formed by gases, among which nitrogen and oxygen stand out, which are present in the atmosphere.
- Smoke (solid in gas). It is a solution in which air acts as a solvent and is generated after combustion.
- Alloys between metals (solid on solid). They are mixtures that occur between metals. For example, duralumin is an aluminum, copper, manganese, magnesium, and silicon alloy.
- Atmospheric dust from the air (solid in gas). It is a solution formed by the gas’s presence of solids (dust particles).
- Steel (solid on solid). It is an alloy between iron and carbon, with a much higher proportion of the first element, which is used in manufacturing machines and tools.
- Carbonated drink (gas in liquid). It is commonly called “gaseous” and is a solution of gases (such as carbonic acid) within a liquid (water).
- Amalgam (liquid in solid). It is an alloy of mercury dissolved in certain metals such as gold or silver and is often used in dentistry.
- Refined oil (liquid in liquid). It is a solution formed after combining elements (the majority is carbon) and is used as fuel.
- Butane in the air (gas on gas). It is the dissolution that occurs between the alkane butane and the air. Butane is a gaseous chemical compound that can be stored in tubes and used as fuel.
- Oxygen in ocean water (gas in liquid). It is the dissolution that occurs between water and oxygen and that allows the development of aquatic life.
- Alcoholic beverage (liquid in liquid). It is a solution of ethanol and fruit juices.
- Coffee with milk (liquid in liquid). It is a solution in which the coffee dissolved in water receives milk, which generates a transformation of its color and flavor.
- Smog (gases in gases). It is a dissolution that occurs from the introducing of gases that are not typical of the atmosphere, which induces a transformation of the air.
- Salt in water (solid in liquid). It is a liquid and homogeneous solution obtained when salt dissolves in water.
- Blood (liquid in liquid). The dissolution occurs between the main component of the blood (plasma) and other elements, such as red blood cells.
- Ammonia in water (liquid in liquid). It is a solution of ammonia and water (which can also be made from a gas to a liquid) that is used in many cleaning supplies.
- Air with traces of moisture (liquid in gas). It is the dissolution that occurs when water vapor is present in the air due to the increase in temperature.
- Powdered juice (solid in liquid). It is a solution obtained when instant juice powder is dissolved in water, and a colored liquid is generated.
- Hydrogen in palladium (gas in solid). It is the solution obtained when hydrogen dissolves in some metals, such as palladium.
- Airborne Viruses (solid in gas). It is a solution that occurs when very small units of a solid are transported by a gas.
- Mercury in silver (liquid in solid). It is one of the so-called “amalgams.”
- Tea (solid in liquid). It is a solution obtained when a solid in very small dimensions (the grains of the tea bag) is dissolved in water.
- Aqua regia (liquid in liquid). It is a composition of acids that allows to dissolve different metals, such as gold.
- Bronze (solid on solid). The alloy between copper and tin is used to make utensils and jewelry in industries such as mining and in the railway and naval transport sectors.
- Lemonade (liquid in liquid). It is a solution made up of lemon juice that dissolves in water.
- Peroxide (liquid in liquid). It is a solution of hydrogen peroxide (HtwoORtwo) in water that is used to disinfect wounds and in the cosmetic industry.
- Ice cooling (solid in liquid). The solution occurs when ice is introduced into the liquid and cools it while it dissolves.
- Physiological saline (solid in liquid). It is a solution formed by sodium chloride and water, which acts as a solvent and is used for the hydration of patients.
- Detergent (liquid in liquid). It is a solution used for cleaning dishes that is made up of elements such as water, alcohol, and sodium sulfonate.
- Smoothie (solids in liquids). It is a substance that is obtained by combining solid foods, such as fruits, and liquids, such as water or milk.
- Sugar water (solids in liquid). It is a solution formed by water and grains of sugar.
- Chocolate milk (solids in liquid). It is a liquid solution obtained by mixing cocoa powder, or chocolate bars, with milk.
- Fragrance. It is a solution that arises from a mixture of different substances, such as water, alcohol, dyes, among others.
- Booze and water (liquid in liquid). It is a liquid solution obtained by mixing alcohol and water. This solution is often used to disinfect surfaces.
- Seawater. It is a solution formed by salts, such as chlorine, magnesium, and sodium, dissolved in water.
- Stainless steel. It is an alloy of iron, carbon and chrome that is characterized by its resistance and non-oxidation. It is used to make kitchen utensils, appliances, furniture, machinery, and surgical instruments.
- Brass. It is an alloy of copper and zinc that is used in locksmithing, jewelry, and electrical components, among others.
- Mouthwash. It is a liquid solution used for oral hygiene, which is usually made up of components such as water, alcohol, and oils, and which helps to eliminate bacteria.
- Clean floors. It is a liquid solution that is used to clean floors and other surfaces and is made up of water, alcohol, and other elements that help eliminate viruses and bacteria.
- Vinegar. It is a liquid solution made up of water and acetic acid that is used to flavor foods and can also be used to clean and disinfect surfaces.
